Waterproof Fabric With Breathable Membrane for Outdoor PPE Kits
How Waterproof and Breathable Membrane Technology Works
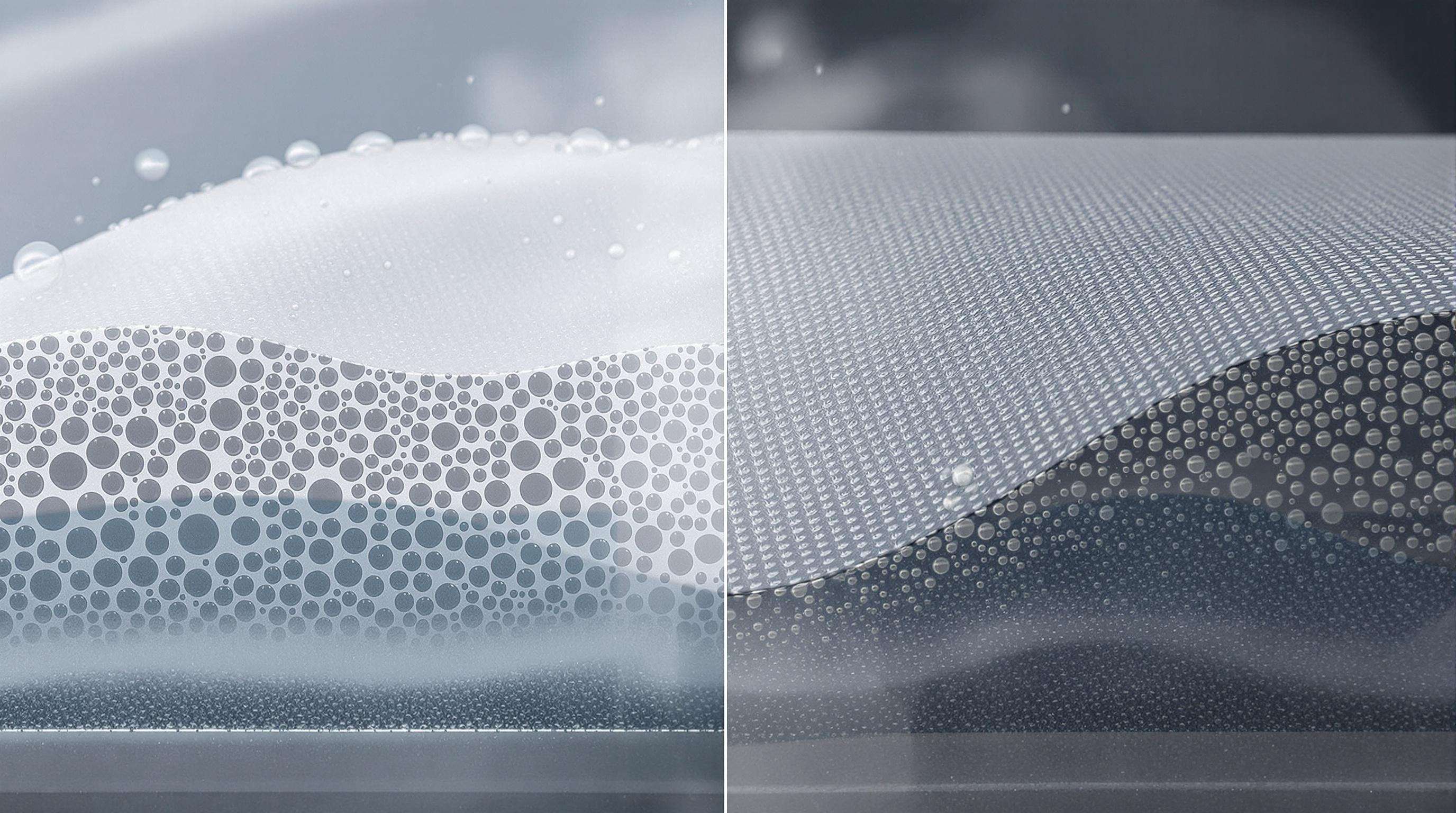
The Science Behind Waterproof and Breathable Fabrics
Waterproof yet breathable fabrics solve the problem of keeping rain out while letting sweat escape from our bodies. Manufacturers accomplish this with special membranes that work in two main ways: tiny pores or moisture loving polymers. Take microporous membranes made from materials like ePTFE for instance. These have literally billions of microscopic holes across each square inch area. The holes are just right sized actually too small for water droplets to get through but big enough so that sweat vapor can pass right on by. On the other hand we have hydrophilic membranes which don't have any pores at all. Instead they absorb moisture and move it along using certain types of polymers that basically drag the vapor molecules through them. Both approaches work best when there's a difference in humidity levels between what's happening inside the garment versus outside conditions. This clever system dates back to the early 70s when researchers first got it working properly. Since then these technologies have become pretty much standard equipment for all sorts of outdoor gear and athletic wear today.
Microporous vs. Hydrophilic Membranes: How They Manage Moisture Transfer
- Microporous membranes (e.g., ePTFE) physically block liquid water using a network of submicron pores while facilitating vapor diffusion. They perform well in high-humidity environments but are susceptible to clogging from surfactants or oils if not properly maintained.
- Hydrophilic membranes use continuous polymer chains to absorb and transport moisture through molecular channels. These membranes offer consistent breathability in contaminated conditions but require specific temperature and humidity gradients to function optimally.
Each system offers distinct advantages: microporous designs provide high breathability under dynamic conditions, while hydrophilic variants excel in durability and resistance to environmental contaminants.
Role of Lamination and Pore Size in Vapor Transmission and Liquid Resistance
The lamination process attaches the membrane to both the outer and inner fabric layers without weakening the overall structure. When it comes to microporous membranes, getting the pore size right matters a lot. Pore sizes ranging from about 0.2 to 5 micrometers strike a good balance between letting air through and keeping liquids out. If pores are bigger than 0.5 micrometers, they allow more moisture vapor to pass through, sometimes as much as 30,000 grams per square meter per day. On the flip side, smaller pores under 2 micrometers do a better job at resisting water pressure, holding up against forces greater than 25,000 millimeters of water column. Adding multiple layers to these laminates makes them tougher against wear and tear while still keeping most of their breathability even after being washed around 50 times. This kind of durability ensures that products perform well over time in tough conditions where regular materials might fail.
Performance Metrics: Comparing Breathability and Waterproof Ratings in Technical Textiles
| Metric | Test Standard | High Performance Range |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability (MVTR) | ISO 11092 | 15,000–30,000 g/m²/24h |
| Waterproofness | ISO 811 | 20,000–40,000 mm |
| Air Permeability | ASTM D737 | <0.5 cfm |
Fabrics achieving MVTR values above 20,000 g/m²/24h and waterproof ratings over 28,000 mm are ideal for extended outdoor use, offering superior protection without sacrificing comfort or mobility.
Gore-Tex and Advanced Membrane Fabrics in Outdoor PPE
Evolution of Gore-Tex and Its Impact on Protective Outdoor Gear
When Gore-Tex first came out back in 1969, it really changed the game for technical clothing. The material uses something called expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (or ePTFE for short) to make a special membrane. These tiny pores are actually 20,000 times smaller than regular water droplets but still let vapor pass through. So what does this mean? Clothing stays dry on the outside while allowing sweat to escape from within. Pretty impressive stuff! Fast forward to today, around three quarters of all top quality outdoor protective equipment now includes some kind of membrane technology. And guess what? Gore-Tex continues to be one of the main standards people look at when talking about how long things last and how well they perform overall. At least that's what the latest Outdoor Gear Innovation Report from 2024 tells us.
Performance of Gore-Tex in Extreme Weather and High-Altitude Environments
The waterproof rating for Gore-Tex stands at around 28,000 mm, which means it can handle about 28 liters per square meter of water pressure before leaking. When it comes to breathability, the fabric lets through approximately 15,000 grams of moisture per square meter every 24 hours. Field tests conducted at high altitudes showed that this material holds up remarkably well even when temperatures drop to minus 40 degrees Celsius and winds reach speeds of 120 kilometers per hour. The material stays flexible enough to move with the body while still providing necessary wind protection for those working in harsh Arctic or mountain environments. According to wind tunnel studies, clothing made with Gore-Tex reduces heat loss by roughly two thirds compared to regular gear without membranes, making a real difference in how warm people stay during cold weather adventures.
Case Study: Gore-Tex Integration in Mountain Rescue and Expedition PPE Kits
Alpine rescue teams now deploy triple-layer Gore-Tex Pro in PPE designed for 72-hour missions. A 2023 study of 120 rescue operations revealed substantial improvements over standard gear:
| Metric | Standard PPE | Gore-Tex PPE |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Retention | 34% | 8% |
| Task Completion Time | 4.2 hours | 3.1 hours |
| Post-Operation Dry Time | 90 minutes | 40 minutes |
Rescue units also report 40% faster drying times in wet snow conditions compared to earlier laminated fabrics, underscoring the material's superiority in moisture management and operational readiness.
Innovations in Lightweight, Flexible Membrane Laminated Fabrics for Mobility and Comfort
Manufacturers today can create membranes weighing just 12 grams per square meter, which is actually lighter than regular printer paper. These materials incorporate graphene doped layers that help regulate temperature and directional stretch fabrics allowing for about 270 degree shoulder movement. The combination makes these composite laminates really useful for things like firefighter suits and military equipment where being able to move freely matters a lot. Testing has shown these materials survive well over 500 abrasion tests according to EN 530:2019 standards while keeping nearly all their water resistance properties intact at 99.8%. That kind of performance makes them great choices for PPE that needs to last through repeated use. The 2023 Industrial Safety Review highlighted this finding among other recent advancements in protective clothing technology.
Real-World Applications in Outdoor and Military PPE
Use of Waterproof Breathable Fabric in Mountaineering and Expedition Gear
When climbers face brutal conditions such as -40 degrees Celsius at 28,000 feet elevation, modern breathable waterproof fabrics still handle impressive amounts of sweat output around 15 liters per square meter every 24 hours without compromising their waterproof properties. The challenge gets tougher though because at those altitudes where air pressure drops significantly, these materials actually transmit about 30 percent less moisture vapor than they would at sea level. However manufacturers have developed better membrane technologies that keep moisture moving out effectively enough so mountaineers can maintain their strength and endurance on long climbs. This was confirmed recently in the latest edition of the Alpine Gear Report from 2023 which tested various gear under similar harsh conditions.
Effectiveness in Military-Grade Protective Clothing Under Extreme Conditions
Troops operating in jungles need gear that works when humidity hits 95% and still blocks chemicals from getting through. Field testing has shown these special fabrics stay dry, holding under 1% moisture even after wearing them nonstop for three whole days. That matters a lot because hypothermia sets in fast when body temps drop just 4 degrees Celsius below normal, which can really mess up someone's ability to fight or survive. The protection offered by these materials makes all the difference during missions across tough terrain and extreme weather conditions. A recent report from the Defense Materials Study in 2024 backs this up, showing why such performance specs are so important for military readiness.
Field Data on Thermal Regulation, Comfort, and Long-Duration Wear Performance
- Thermal regulation: Maintains core body temperature within 32–35°C during 8-hour Arctic patrols
- Comfort: Achieves 40% faster sweat evaporation compared to traditional coated fabrics (2024 Field Performance Review)
- Durability: Retains 98% waterproof performance after 50+ abrasion cycles (ISO 12947)
These metrics confirm that modern membrane technologies support 120-hour continuous wear across multiple environments while meeting the 10,000 mm hydrostatic head threshold required for storm-level weather resistance.
Durability, Longevity, and Environmental Resistance of Protective Membranes

Testing Standards for Abrasion Resistance, Seam Strength, and Waterproof Integrity
The best performing membranes go through strict international testing protocols. Standards like ISO 4914 check how well they resist wear and tear, ASTM D751 measures their ability to hold back water pressure, and EN 14360 looks at how strong the seams really are. When we talk about top quality personal protective equipment, these products can handle more than 15 thousand cycles on the Martindale abrasion test machine. They also keep water out as if there was a whole 40 meter column of water pressing against them, which works out to around 28 pounds per square inch. The stitching between panels gets special treatment too. These taped seams need to stand up to about 1.8 kilonewtons of pulling force before they start coming apart. That kind of strength means workers won't have problems with their gear falling apart when moving around or bending in tough conditions.
Impact of UV Exposure, Chemicals, and Repeated Use on Membrane Performance
According to a recent 2024 study on material longevity, fabrics coated with polyurethane hold onto about 92% of their water resistance even after being exposed to UV light for 1,200 straight hours under ASTM G154 standards. That's actually pretty impressive when compared to PTFE membranes which only managed around 74% retention in similar conditions. When it comes to fluoropolymer treatments, these materials show good resilience too, standing up against over fifty industrial detergent wash cycles while keeping pore degradation below 7%. But there's a catch worth noting here. If someone keeps washing these materials with polar solvents repeatedly, moisture vapor transmission rates drop by roughly 22% after just seventy five washes. This clearly shows why following manufacturer recommended cleaning procedures matters so much for maintaining fabric performance over time.
Balancing Long-Term Breathability and Waterproof Protection in Reusable PPE
Advanced laminated membranes maintain 95% MVTR retention (≥15,000 g/m²/24h) over 50+ use cycles through innovative design features:
- Gradient pore architectures (20–50 μ outer layer, 0.2–5 μ inner layer)
- Hydrophobic matrix reinforcement with <1% swell index
- Sacrificial coating technologies that self-heal micro-abrasions
Field data from alpine rescue teams show trilayer ePTFE membranes sustain 28 kPa waterproof pressure and deliver consistent 18,000 g/m²/24h breathability after 200 operational days—critical for preventing heat stress and ensuring reliability during extended missions.
FAQ
What makes a fabric waterproof yet breathable?
Waterproof yet breathable fabrics use special membranes that either have tiny pores or moisture-loving polymers. Microporous membranes like ePTFE have billions of microscopic holes that block water droplets while allowing sweat vapor to pass. Hydrophilic membranes do not contain pores but absorb moisture and transport it using polymers.
How does pore size affect waterproof and breathable membranes?
Pore size is crucial for balancing vapor transmission and liquid resistance. Microporous membranes with pore sizes ranging from 0.2 to 5 micrometers allow air through while blocking liquids. Proper pore size ensures durability and resistance to water pressure while maintaining breathability.
Why is Gore-Tex considered a standard in outdoor protective gear?
Gore-Tex uses expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) membranes that are highly effective at being waterproof and breathable. It remains a standard due to its durability, excellent moisture management, and reliability in extreme conditions, as evidenced by extensive field testing and industry reports.
How do advanced membranes maintain durability and performance over time?
Advanced laminated membranes maintain their performance with gradient pore architectures, hydrophobic matrix reinforcement, and sacrificial coating technologies. These features offer self-healing properties, resistance to environmental factors, and sustained breathability and waterproofness over many use cycles.

 EN
EN





































